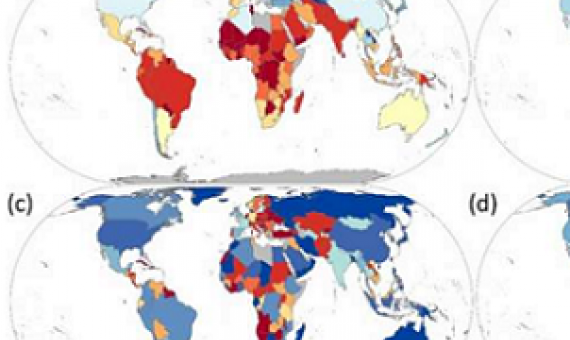
Climate benefits from establishing marine protected areas targeted at blue carbon solutions
Marine protected areas (MPAs) are recognized as highly effective tools for marine conservation. They may also play an important role in mitigating climate change. A variety of climate change solutions are rooted in the ocean, centered primarily around “blue carbon” and the capacity of marine life to sequester carbon dioxide (CO2) with some potential to reduce emissions. However, the global potential of these solutions remains misunderstood and untapped.